Decoding The Periodic Desk: A Deep Dive Into Atomic Dimension And Its Traits
Decoding the Periodic Desk: A Deep Dive into Atomic Dimension and its Traits
Associated Articles: Decoding the Periodic Desk: A Deep Dive into Atomic Dimension and its Traits
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Periodic Desk: A Deep Dive into Atomic Dimension and its Traits. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Periodic Desk: A Deep Dive into Atomic Dimension and its Traits

The periodic desk, a seemingly easy association of parts, holds a wealth of details about the basic constructing blocks of matter. Probably the most essential, but usually ignored, properties depicted inside its construction is atomic measurement. Understanding atomic measurement and its tendencies is vital to comprehending chemical reactivity, bonding habits, and quite a few different bodily and chemical properties. This text will discover the idea of atomic measurement, the components influencing it, and the way it varies throughout the periodic desk, illustrated with detailed explanations and examples.
Defining Atomic Dimension: A Matter of Perspective
Defining atomic measurement is not easy. Atoms haven’t got sharply outlined boundaries like macroscopic objects. Their electron clouds progressively fade into area. Subsequently, completely different strategies are used to measure atomic measurement, resulting in barely completely different values relying on the approach employed. Generally used measures embody:
- Covalent Radius: Half the gap between the nuclei of two similar atoms bonded collectively covalently. That is appropriate for non-metals and a few metalloids.
- Metallic Radius: Half the gap between the nuclei of two adjoining atoms in a metallic crystal lattice. That is relevant to metals.
- Van der Waals Radius: Half the gap between the nuclei of two similar, non-bonded atoms in shut proximity. This methodology is used for atoms the place covalent or metallic radii aren’t relevant.
Whereas the exact values could differ barely primarily based on the tactic, the general tendencies throughout the periodic desk stay constant. It is essential to do not forget that these radii are averages, and the precise distance between atoms can fluctuate as a consequence of components like bonding sort and surrounding setting.
Components Influencing Atomic Dimension
A number of components interaction to find out the dimensions of an atom:
-
Nuclear Cost (Variety of Protons): A higher variety of protons within the nucleus exerts a stronger optimistic cost, attracting the electrons extra strongly and pulling them nearer to the nucleus. This leads to a smaller atomic radius.
-
Shielding Impact (Variety of Internal Electrons): Internal electrons defend the outer valence electrons from the complete enticing power of the nucleus. Because the variety of internal electrons will increase, the efficient nuclear cost skilled by the valence electrons decreases, resulting in a bigger atomic radius. This impact is especially pronounced in parts with a number of electron shells.
-
Principal Quantum Quantity (n): This quantum quantity represents the power stage of an electron and its distance from the nucleus. Greater principal quantum numbers point out bigger orbitals and due to this fact a bigger atomic radius. As you progress down a gaggle within the periodic desk, the principal quantum quantity will increase, resulting in a major improve in atomic measurement.
-
Electron-Electron Repulsion: Electrons repel one another. In atoms with a number of valence electrons, the repulsion between these electrons can counteract the enticing power of the nucleus, barely rising the atomic radius. This impact is much less important than the nuclear cost and shielding results.
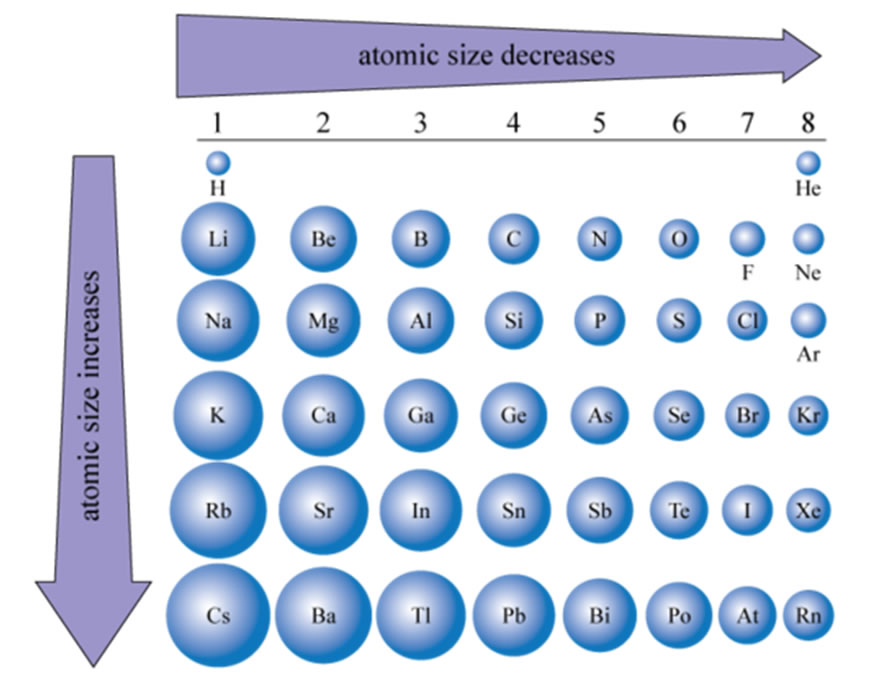
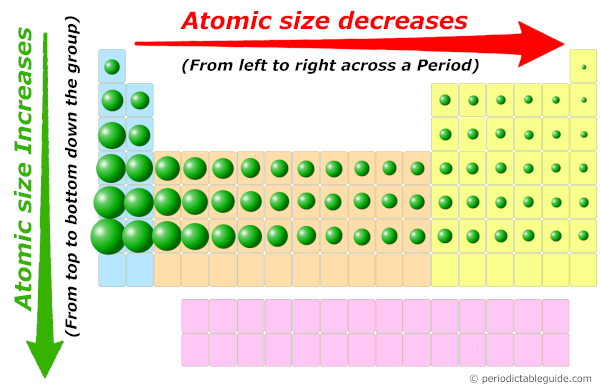
Traits in Atomic Dimension throughout the Periodic Desk
The interaction of those components creates predictable tendencies in atomic measurement as we traverse the periodic desk:
-
Throughout a Interval (Left to Proper): Atomic measurement typically decreases as you progress from left to proper throughout a interval. That is primarily because of the rising nuclear cost. Whereas the variety of electrons additionally will increase, they’re added to the identical principal power stage, and the shielding impact stays comparatively fixed. The stronger nuclear attraction outweighs the electron-electron repulsion, resulting in a smaller atomic radius.
-
Down a Group (High to Backside): Atomic measurement typically will increase as you progress down a gaggle. It is because every successive factor provides electrons to a brand new, larger principal power stage, considerably rising the gap of the valence electrons from the nucleus. The rise in shielding impact additionally contributes to this growth.
Illustrative Examples:
Let’s contemplate some particular examples to spotlight these tendencies:
-
Interval 3 (Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar): The atomic radius decreases from sodium (Na) to argon (Ar). Sodium has the biggest radius, whereas argon has the smallest.
-
Group 1 (Alkali Metals): The atomic radius will increase considerably as you progress down the group from lithium (Li) to francium (Fr). Francium has the biggest atomic radius among the many alkali metals.
-
Comparability: Li and F: Lithium (Li) is considerably bigger than fluorine (F) regardless of being in the identical interval. Fluorine has a a lot larger nuclear cost, outweighing the marginally larger electron-electron repulsion, leading to a smaller atomic radius.
-
Comparability: Li and Na: Lithium (Li) is smaller than sodium (Na) as a result of sodium has an extra electron shell (n=3) in comparison with lithium (n=2).
Exceptions and Anomalies:
Whereas the overall tendencies are well-established, there are some exceptions and anomalies. These deviations could be attributed to delicate variations in electron configurations, electron-electron repulsions, and different quantum mechanical results. For example, the slight improve in atomic radius noticed between sure transition metals could be defined by the gradual filling of d-orbitals and the complicated interaction of electron-electron shielding.
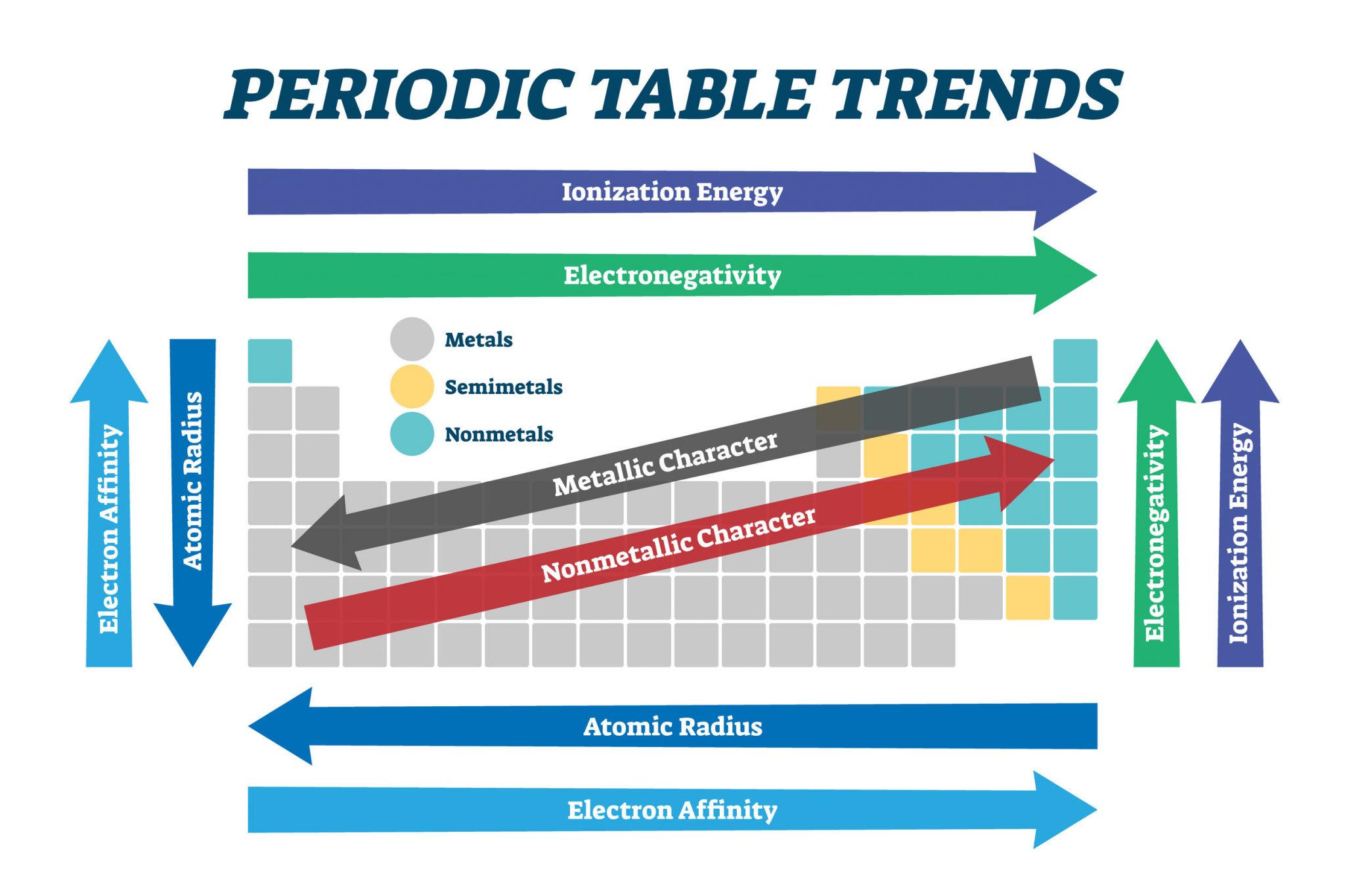
Functions and Significance of Atomic Dimension
Understanding atomic measurement is essential in varied fields:
-
Chemical Bonding: Atomic measurement influences bond size and bond energy. Smaller atoms are inclined to type stronger bonds.
-
Chemical Reactivity: Atomic measurement performs a major function in figuring out a component’s reactivity. Bigger atoms usually have decrease ionization energies and better electronegativities, influencing their tendency to lose or acquire electrons.
-
Materials Science: Atomic measurement is vital in designing supplies with particular properties. For instance, the dimensions of atoms influences the crystal construction and properties of alloys.
-
Catalysis: The scale and form of atoms and molecules affect their means to behave as catalysts.
-
Nuclear Chemistry: Atomic measurement is related in understanding nuclear reactions and interactions.
Conclusion:
Atomic measurement, whereas seemingly a easy idea, is a elementary property that considerably impacts the habits of parts and their compounds. The systematic tendencies noticed within the periodic desk, pushed by nuclear cost, shielding impact, and principal quantum quantity, present a robust framework for understanding and predicting the properties of matter. Though exceptions exist, the general tendencies stay remarkably constant, making the examine of atomic measurement a vital part of chemical understanding. By greedy these tendencies, we will unlock deeper insights into the intricacies of the chemical world and its functions in numerous fields. Additional exploration into the complexities of atomic construction and quantum mechanics supplies a richer understanding of the nuances behind these periodic tendencies and their affect on the macroscopic world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Decoding the Periodic Desk: A Deep Dive into Atomic Dimension and its Traits. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!
