Decoding The Decade: A Deep Dive Into The ten-12 months Treasury Yield
Decoding the Decade: A Deep Dive into the 10-12 months Treasury Yield
Associated Articles: Decoding the Decade: A Deep Dive into the 10-12 months Treasury Yield
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Decade: A Deep Dive into the 10-12 months Treasury Yield. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Decade: A Deep Dive into the 10-12 months Treasury Yield

The ten-year Treasury yield, a seemingly obscure monetary metric, acts as a strong barometer of the US economic system and international monetary markets. This benchmark rate of interest, representing the return traders obtain on a 10-year US authorities bond, influences all the pieces from mortgage charges and company borrowing prices to the worth of the greenback and the course of inventory markets. Understanding its actions over the previous decade, and the components driving these actions, is essential for navigating the advanced panorama of recent finance.
A Decade of Volatility: 2013-2023
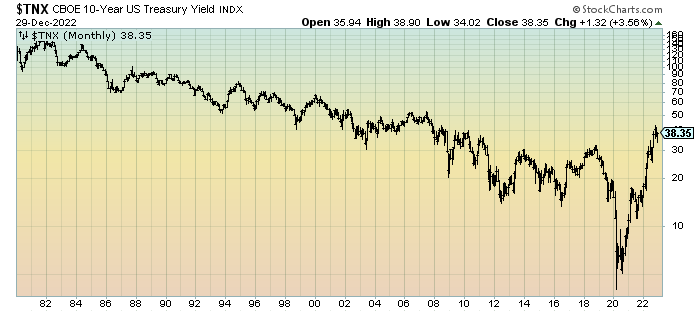
The previous decade has witnessed a dramatic rollercoaster trip for the 10-year Treasury yield. Beginning round 2% in early 2013, following the aftermath of the 2008 monetary disaster and the following quantitative easing (QE) applications carried out by the Federal Reserve, the yield regularly rose and fell in response to numerous financial and geopolitical occasions.
The interval between 2013 and 2016 noticed a comparatively subdued yield, fluctuating between 1.5% and a couple of.5%. This era was characterised by gradual financial development, low inflation, and continued accommodative financial coverage from the Fed. The low yields mirrored investor confidence within the security and stability of US authorities debt, regardless of considerations about international financial fragility.
A big shift occurred in 2017 and 2018, because the US economic system gained momentum underneath the Trump administration’s tax cuts and elevated authorities spending. This led to expectations of upper inflation and stronger financial development, pushing the 10-year yield steadily upwards, peaking close to 3.2% in late 2018. This rise, nonetheless, was met with market jitters, as traders apprehensive concerning the potential for overheating and the Fed’s subsequent tightening of financial coverage.
The 12 months 2019 introduced a reversal, with the 10-year yield falling again beneath 2% amidst international financial slowdown, commerce tensions with China, and a renewed sense of uncertainty within the markets. The Fed, responding to those considerations, adopted a extra dovish stance, signaling a possible pause and even reversal of its price hike cycle.
The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 triggered an unprecedented plunge within the 10-year yield, falling to a file low beneath 0.5%. This dramatic drop mirrored the large fiscal and financial stimulus unleashed by the federal government and the Fed to mitigate the financial fallout from the pandemic. Buyers flocked to the protection of US Treasuries, driving down yields regardless of the elevated authorities borrowing.
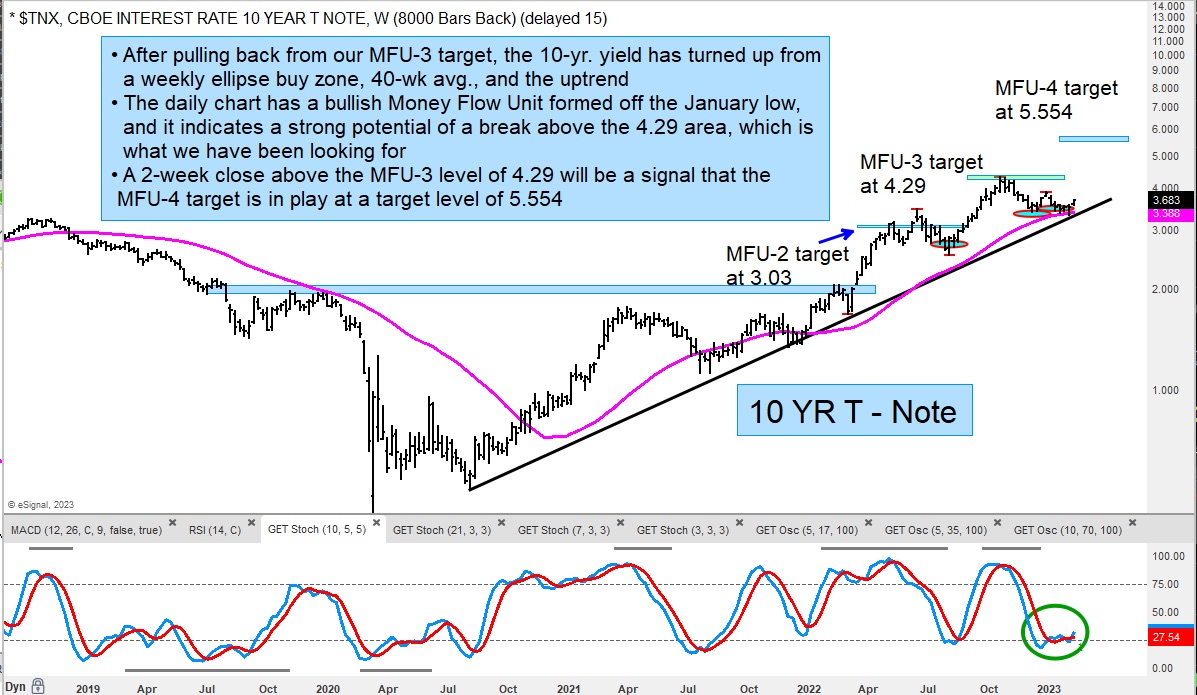
The following restoration in 2021 and 2022 noticed a big rebound within the 10-year yield, climbing above 4% at its peak. This surge was pushed by a mixture of things, together with strong financial development, provide chain disruptions fueling inflation, and the Fed’s aggressive tightening of financial coverage to fight rising inflation. The speedy enhance in yields led to considerations concerning the potential for a pointy financial slowdown or perhaps a recession.
By late 2023, the yield has proven indicators of stabilization, though it stays elevated in comparison with pre-pandemic ranges. The longer term trajectory of the yield stays unsure, depending on a large number of interacting financial and geopolitical components.
Key Components Influencing the 10-12 months Treasury Yield:
A number of interconnected components contribute to the fluctuations within the 10-year Treasury yield:
-
Inflation Expectations: Greater inflation expectations typically result in increased yields, as traders demand the next return to compensate for the erosion of buying energy. The inflation price, as measured by indices just like the Client Value Index (CPI) and the Private Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index, performs an important position in shaping inflation expectations.
-
Federal Reserve Coverage: The Federal Reserve’s financial coverage selections considerably affect Treasury yields. Elevating rates of interest (a tightening of financial coverage) usually pushes yields increased, whereas reducing charges (loosening financial coverage) tends to push them decrease. The Fed’s communication relating to its future coverage intentions additionally performs a big position in market expectations and yield actions.
-
Financial Development: Sturdy financial development usually results in increased yields, as elevated demand for credit score pushes rates of interest up. Conversely, weak financial development can result in decrease yields as traders search safer havens. Key financial indicators like GDP development, employment figures, and client spending present insights into the general financial well being and affect yield actions.
-
International Financial Situations: International financial occasions and geopolitical dangers can considerably affect the 10-year Treasury yield. Uncertainty in international markets usually leads traders to hunt the protection of US Treasuries, driving down yields. Conversely, sturdy international development can result in increased yields as traders search increased returns elsewhere.
-
Provide and Demand: The provision of Treasury bonds and the demand for them additionally affect yields. Elevated authorities borrowing to finance deficits can enhance the availability of bonds, probably pushing yields increased. Conversely, sturdy demand for US Treasuries, pushed by components like investor confidence or safe-haven searching for, can push yields decrease.
-
Fiscal Coverage: Authorities spending and taxation insurance policies can not directly affect Treasury yields. Elevated authorities spending financed by borrowing can enhance the availability of bonds, probably elevating yields. Tax insurance policies also can have an effect on financial development and inflation, influencing yields not directly.
The ten-12 months Yield as a Main Indicator:
The ten-year Treasury yield is commonly thought-about a number one indicator of future financial exercise. Its actions can present precious insights into market expectations relating to future inflation, financial development, and financial coverage. As an example, a rising yield can sign expectations of stronger financial development and better inflation, whereas a falling yield can counsel considerations about financial slowdown or deflation.
Nonetheless, it is essential to keep in mind that the 10-year yield is only one piece of the puzzle. Analyzing it along side different financial indicators and market alerts gives a extra complete understanding of the financial outlook.
Implications for Buyers and Companies:
The ten-year Treasury yield has important implications for varied market contributors:
-
Fastened-Revenue Buyers: The yield instantly impacts the returns on fixed-income investments, together with bonds and different debt devices. Greater yields provide increased returns but in addition carry increased danger, whereas decrease yields provide decrease returns however decrease danger.
-
Mortgage Debtors: Mortgage charges are sometimes intently tied to the 10-year Treasury yield. Greater yields usually result in increased mortgage charges, making homeownership dearer.
-
Company Debtors: The yield serves as a benchmark for company borrowing prices. Greater yields typically result in increased borrowing prices for firms, impacting their funding selections and profitability.
-
Forex Markets: The ten-year Treasury yield influences the worth of the US greenback. Greater yields have a tendency to draw international funding, strengthening the greenback, whereas decrease yields can weaken it.
Conclusion:
The ten-year Treasury yield is a fancy and dynamic metric, reflecting the interaction of assorted financial and geopolitical components. Understanding its historic actions, the components driving these actions, and its implications for various market contributors is essential for knowledgeable decision-making within the monetary world. Whereas the previous decade has offered precious classes, predicting the long run trajectory of the yield stays a difficult, but important, job for traders, companies, and policymakers alike. Continued monitoring and evaluation of the yield, along side different financial knowledge, are important for navigating the complexities of the worldwide monetary panorama. The ten-year Treasury yield, removed from being an obscure metric, serves as an important key to understanding the heart beat of the worldwide economic system.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Decoding the Decade: A Deep Dive into the 10-12 months Treasury Yield. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!