Decoding The Bar Chart: A Complete Information With Examples
Decoding the Bar Chart: A Complete Information with Examples
Associated Articles: Decoding the Bar Chart: A Complete Information with Examples
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Bar Chart: A Complete Information with Examples. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Bar Chart: A Complete Information with Examples

Bar charts, a cornerstone of knowledge visualization, present a transparent and concise solution to examine completely different classes of knowledge. Their simplicity belies their versatility, making them an indispensable instrument for presenting data throughout various fields, from enterprise analytics and scientific analysis to training and on a regular basis life. This text delves into the intricacies of bar charts, exploring their numerous varieties, purposes, strengths, weaknesses, and providing quite a few examples as an example their sensible use.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What’s a Bar Chart?
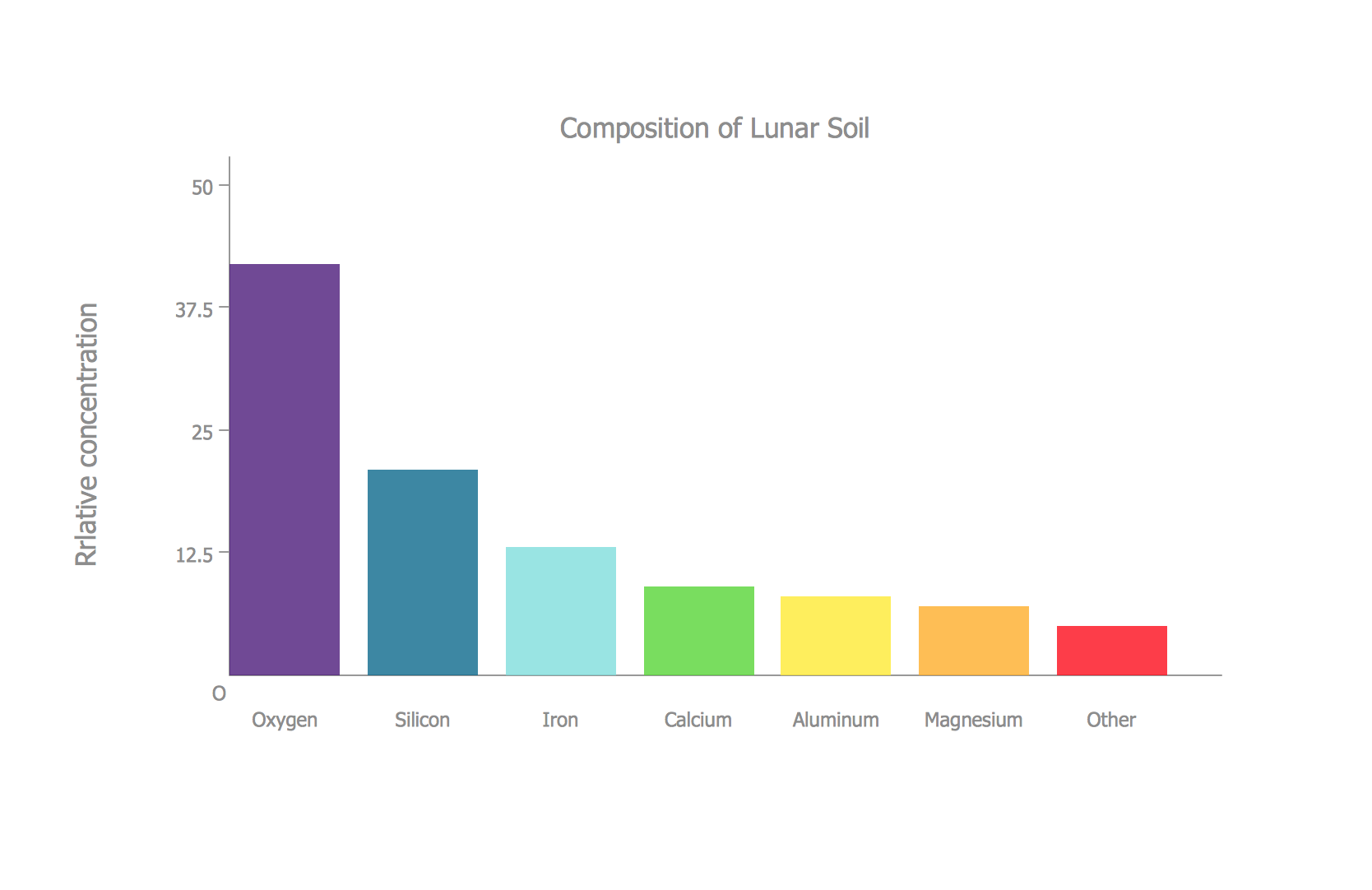
A bar chart, also called a bar graph, is a pictorial illustration of knowledge that makes use of rectangular bars of various lengths to show the magnitude of various classes. The size of every bar is instantly proportional to the worth it represents. This visible comparability permits for fast and simple understanding of relative sizes and variations between information factors. The chart sometimes has two axes: a horizontal (x-axis) and a vertical (y-axis). The x-axis represents the classes being in contrast, whereas the y-axis represents the values or portions related to every class.
Sorts of Bar Charts:
A number of variations of bar charts exist, every designed to greatest symbolize particular information buildings and reply explicit questions. The most typical varieties embody:
-
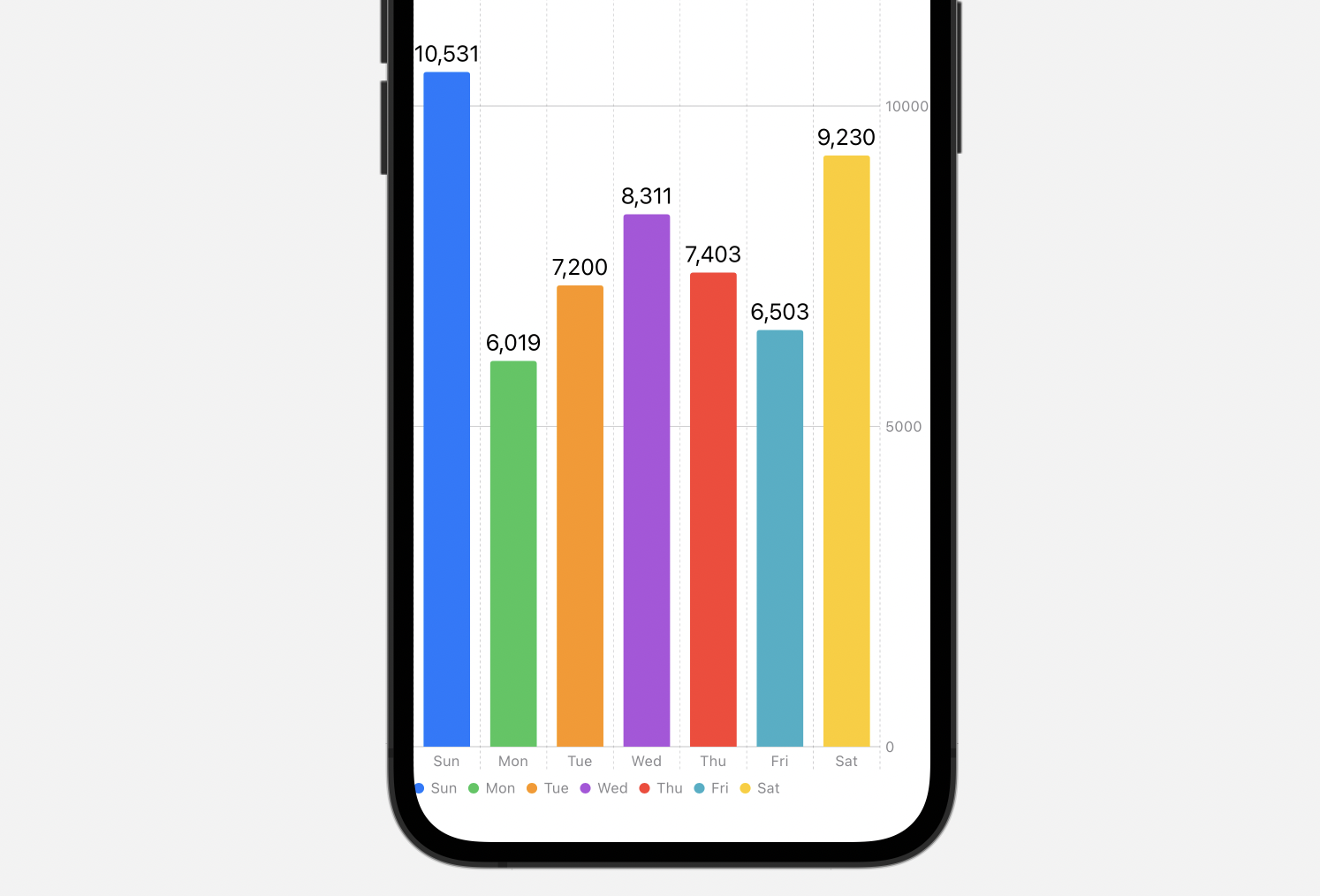
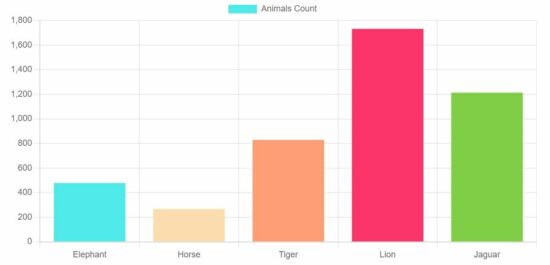
Vertical Bar Chart: That is essentially the most regularly used sort, with classes listed alongside the horizontal axis and their corresponding values represented by the peak of the vertical bars. This format is mostly most popular when evaluating a comparatively small variety of classes.
-
Horizontal Bar Chart: Much like the vertical bar chart, however classes are listed alongside the vertical axis, and the lengths of the horizontal bars symbolize the values. Horizontal bar charts are notably helpful when class labels are lengthy or quite a few, as they keep away from overlapping textual content.
-
Clustered Bar Chart (Grouped Bar Chart): This chart shows a number of information sequence for every class, with bars clustered collectively to facilitate comparisons inside and throughout classes. For instance, it may present gross sales figures for various merchandise throughout a number of months.
-
Stacked Bar Chart: Much like the clustered bar chart, however as an alternative of putting bars side-by-side, the info sequence for every class are stacked on high of one another inside a single bar. This kind is efficient in exhibiting the composition of every class’s complete worth. As an illustration, it may illustrate the breakdown of bills into completely different classes for a particular challenge.
-
100% Stacked Bar Chart: A variation of the stacked bar chart the place the overall top of every bar is normalized to 100%, representing the proportion of every information sequence throughout the class. This emphasizes the relative contribution of every element.
Examples of Bar Chart Purposes:
The flexibility of bar charts makes them appropriate for a variety of purposes:
-
Enterprise Analytics: Evaluating gross sales figures throughout completely different areas, product efficiency, advertising marketing campaign effectiveness, buyer demographics, and extra.
-
Scientific Analysis: Presenting experimental outcomes, evaluating remedy teams, illustrating statistical information, and showcasing analysis findings.
-
Schooling: Displaying scholar efficiency, evaluating check scores, illustrating class demographics, and visualizing academic developments.
-
Finance: Representing funding returns, evaluating inventory costs, showcasing monetary ratios, and illustrating finances allocations.
-
Healthcare: Illustrating illness prevalence, evaluating remedy outcomes, exhibiting affected person demographics, and visualizing healthcare useful resource allocation.
-
Social Sciences: Presenting survey outcomes, evaluating demographic information, illustrating social developments, and visualizing analysis findings.
Instance 1: Evaluating Gross sales of Completely different Merchandise
To illustrate an organization sells three merchandise: A, B, and C. The gross sales figures for the final quarter are:
- Product A: 150 items
- Product B: 200 items
- Product C: 100 items
A vertical bar chart would successfully symbolize this information. The x-axis would listing the merchandise (A, B, C), and the y-axis would symbolize the variety of items offered. Every product would have a corresponding bar, with the peak reflecting the variety of items offered. Product B would have the tallest bar, indicating the best gross sales.
Instance 2: Exhibiting Month-to-month Web site Site visitors
Think about an internet site proprietor desires to trace their web site site visitors over six months. The info is:
- January: 1000 guests
- February: 1200 guests
- March: 1500 guests
- April: 1300 guests
- Might: 1800 guests
- June: 2000 guests
A horizontal bar chart could possibly be used right here. The months could be listed on the y-axis, and the variety of guests could be represented by the size of the horizontal bars. This enables for clear readability of the month names, even with a bigger variety of classes.
Instance 3: Analyzing Buyer Preferences
An organization conducts a survey to grasp buyer preferences for various options of their product. The outcomes are:
- Function X: 60% choice
- Function Y: 25% choice
- Function Z: 15% choice
A 100% stacked bar chart could be best. A single bar represents 100% of buyer preferences, with segments throughout the bar representing the proportion of consumers preferring every characteristic. This clearly exhibits the relative recognition of every characteristic.
Instance 4: Evaluating Gross sales Throughout Areas (Clustered Bar Chart)
An organization desires to match the gross sales of two merchandise (Product X and Product Y) throughout three areas (North, South, East). The info is:
- North: Product X – 50, Product Y – 70
- South: Product X – 80, Product Y – 60
- East: Product X – 60, Product Y – 90
A clustered bar chart would effectively symbolize this information. Every area could be represented on the x-axis, and two bars could be clustered collectively for every area, one representing the gross sales of Product X and the opposite for Product Y. This enables for simple comparability of gross sales for every product throughout completely different areas.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Bar Charts:
Strengths:
- Straightforward to grasp and interpret: Their visible nature makes them accessible to a large viewers, no matter their statistical experience.
- Efficient for evaluating classes: They excel at showcasing relative variations between completely different information factors.
- Versatile: Numerous varieties cater to completely different information buildings and analytical wants.
- Straightforward to create: Quite a few software program packages and instruments facilitate the creation of bar charts.
Weaknesses:
- Restricted to categorical information: They aren’t appropriate for representing steady information.
- Will be deceptive if not correctly scaled: Incorrect scaling can distort the notion of knowledge variations.
- Can change into cluttered with many classes: For numerous classes, various visualization strategies may be simpler.
- Would not present detailed developments over time: For temporal information, line charts are typically extra acceptable.
Conclusion:
Bar charts are highly effective instruments for information visualization, providing a easy but efficient solution to examine and distinction completely different classes of knowledge. Their versatility and ease of interpretation make them invaluable throughout a variety of purposes. By understanding the various kinds of bar charts and their strengths and weaknesses, one can successfully leverage them to speak information insights clearly and concisely. Choosing the proper sort of bar chart depends upon the particular information and the message you need to convey. Cautious consideration of knowledge illustration and chart design ensures correct and impactful communication of knowledge.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Decoding the Bar Chart: A Complete Information with Examples. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!