Decoding M³: A Complete Information To Cubic Meters In Measurement Charts
Decoding m³: A Complete Information to Cubic Meters in Measurement Charts
Associated Articles: Decoding m³: A Complete Information to Cubic Meters in Measurement Charts
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Decoding m³: A Complete Information to Cubic Meters in Measurement Charts. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding m³: A Complete Information to Cubic Meters in Measurement Charts
The standard "m³," usually seen in measurement charts and technical specs, represents a basic unit of quantity within the metric system. Understanding its which means and software is essential throughout numerous fields, from building and engineering to delivery and agriculture. This text delves deep into the which means of m³ (cubic meters), exploring its calculation, sensible functions, conversions, and customary misconceptions.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What’s a Cubic Meter?
A cubic meter (m³) is the quantity occupied by a dice with sides measuring one meter (1m) in size. Think about a wonderfully sq. field; if all sides of that field measures one meter, then the quantity enclosed inside that field is one cubic meter. This seemingly easy idea kinds the premise for measuring the quantity of an unlimited array of objects and areas.
The significance of understanding cubic meters lies in its capability to offer a standardized unit for quantifying three-dimensional area. Not like linear measurements (like meters or ft), which solely describe one dimension, cubic meters embody size, width, and peak, offering a whole image of the area’s capability.
Calculating Cubic Meters: Strategies and Purposes
Calculating the quantity in cubic meters depends upon the form of the article or area being measured. Listed here are some widespread eventualities and their corresponding calculation strategies:
-
Common Shapes (Cuboids, Cubes): For often formed objects like cubes and cuboids (rectangular prisms), the calculation is easy:
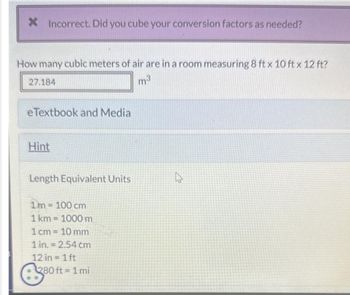
Quantity (m³) = Size (m) x Width (m) x Top (m)For instance, a room measuring 4 meters lengthy, 3 meters extensive, and a couple of.5 meters excessive would have a quantity of:
4m x 3m x 2.5m = 30 m³ -
Irregular Shapes: Measuring the quantity of irregularly formed objects requires extra subtle methods. Widespread strategies embrace:
- Water Displacement: Submerging the article in a container of identified quantity and measuring the change in water stage gives a direct measurement of the article’s quantity. This technique is especially helpful for oddly formed objects.
- Geometric Approximation: Breaking down an irregular form into smaller, common shapes (cubes, prisms, and many others.) permits for an approximate calculation of the entire quantity. The accuracy of this technique depends upon the precision of the approximation.
- 3D Scanning: Superior applied sciences like 3D scanning present extremely correct digital fashions of objects, permitting for exact quantity calculations utilizing specialised software program.
-
Particular Purposes: The calculation of cubic meters is significant in quite a few fields:
- Building: Estimating the quantity of concrete, earthworks, or different supplies wanted for a challenge.
- Delivery and Logistics: Figuring out the cargo capability of containers, vehicles, or ships. That is essential for environment friendly transportation and price administration.
- Agriculture: Measuring the quantity of grain silos, fertilizer storage, or irrigation water.
- Environmental Science: Calculating the quantity of pollution in a physique of water or the quantity of landfill area required.
- HVAC (Heating, Air flow, and Air Conditioning): Figuring out the dimensions of air ducts and the quantity of air to be conditioned in a constructing.
Conversions and Items: Navigating the Metric System
Whereas m³ is the usual unit for quantity within the metric system, different associated models are incessantly encountered:
- Liters (L): 1 m³ = 1000 L. Liters are generally used for smaller volumes of liquids.
- Cubic Centimeters (cm³): 1 m³ = 1,000,000 cm³. Cubic centimeters are helpful for measuring smaller objects.
- Cubic Millimeters (mm³): 1 m³ = 1,000,000,000 mm³. Cubic millimeters are used for very small volumes.
Changing between these models requires understanding the relationships between them. Conversion elements are available on-line and in lots of reference supplies. For instance, to transform cubic meters to liters, merely multiply the quantity in cubic meters by 1000.
Widespread Misconceptions and Pitfalls
Regardless of its easy idea, a number of misconceptions surrounding cubic meters can result in errors in calculations and functions:
- Complicated Quantity with Space: Space measures two-dimensional area (size x width), whereas quantity measures three-dimensional area (size x width x peak). Failing to differentiate between these ideas is a typical mistake.
- Incorrect Unit Conversions: Inaccurate conversions between cubic meters and different models can considerably have an effect on the outcomes. All the time double-check your conversion elements.
- Neglecting Irregular Shapes: Assuming an irregular form is common can result in substantial errors in quantity calculations. Using applicable measurement methods for irregular shapes is essential.
- Oversimplification of Advanced Situations: Actual-world functions usually contain complicated geometries and a number of supplies. Simplifying these eventualities excessively can result in inaccurate estimations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Cubic Meters
The cubic meter (m³) serves as a cornerstone of quantity measurement within the metric system. Its constant software throughout numerous fields highlights its significance in numerous industries. From designing buildings and transporting items to managing sources and understanding environmental processes, a agency grasp of cubic meters and their calculation is crucial for accuracy, effectivity, and efficient problem-solving. By understanding the basics, using applicable calculation strategies, and avoiding widespread pitfalls, people and professionals can leverage the facility of cubic meters for correct and dependable quantity measurements. Mastering this seemingly easy unit unlocks a deeper understanding of the three-dimensional world round us and the portions that outline it. Additional exploration into specialised functions of cubic meters, reminiscent of these involving fluid dynamics or complicated geological formations, will reveal much more nuanced features of this basic unit of measurement.

-to-cubic-meters.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Decoding m³: A Complete Information to Cubic Meters in Measurement Charts. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!
