Decoding The Z-Desk: A Complete Information To The Normal Regular Distribution Chart
Decoding the Z-Desk: A Complete Information to the Normal Regular Distribution Chart
Associated Articles: Decoding the Z-Desk: A Complete Information to the Normal Regular Distribution Chart
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Z-Desk: A Complete Information to the Normal Regular Distribution Chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Z-Desk: A Complete Information to the Normal Regular Distribution Chart
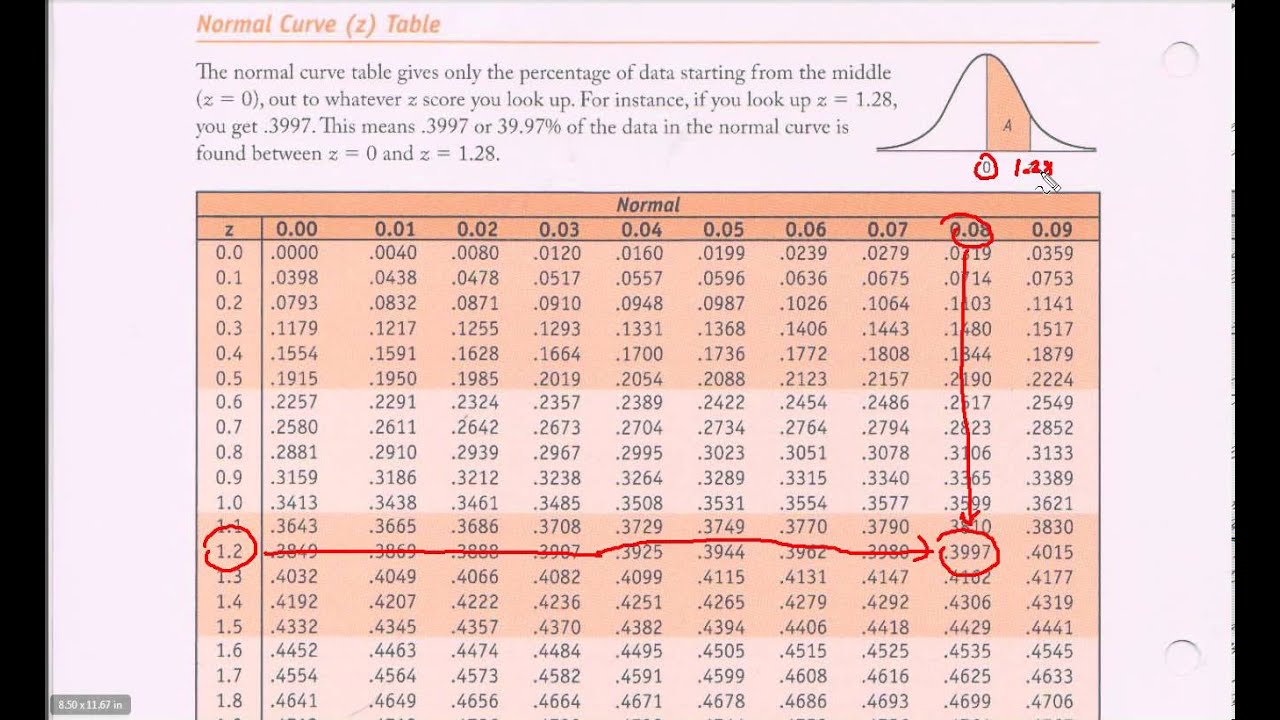
The Z-table, also referred to as the usual regular distribution desk, is a vital instrument in statistics and likelihood. It is an indispensable useful resource for anybody working with usually distributed information, offering the cumulative likelihood related to any given Z-score. Understanding and using the Z-table successfully is prime to varied statistical analyses, from speculation testing and confidence intervals to figuring out possibilities and percentiles. This text gives a complete overview of the Z-table, its development, interpretation, and sensible purposes, complemented by illustrative examples.
Understanding the Normal Regular Distribution:
Earlier than delving into the Z-table itself, it is essential to understand the idea of the usual regular distribution. This can be a particular sort of regular distribution with a imply (μ) of 0 and a normal deviation (σ) of 1. The Z-table is particularly designed for this standardized distribution. The fantastic thing about standardization lies in its capability to transform any usually distributed variable into a normal regular variable (Z-score) utilizing the next method:
Z = (X – μ) / σ
The place:
- Z is the Z-score
- X is the worth of the uncooked information level
- μ is the inhabitants imply
- σ is the inhabitants normal deviation
This transformation permits us to make use of the only Z-table to search out possibilities for any usually distributed variable, no matter its unique imply and normal deviation. The Z-score represents the variety of normal deviations an information level is away from the imply. A constructive Z-score signifies the info level is above the imply, whereas a destructive Z-score signifies it is under the imply.
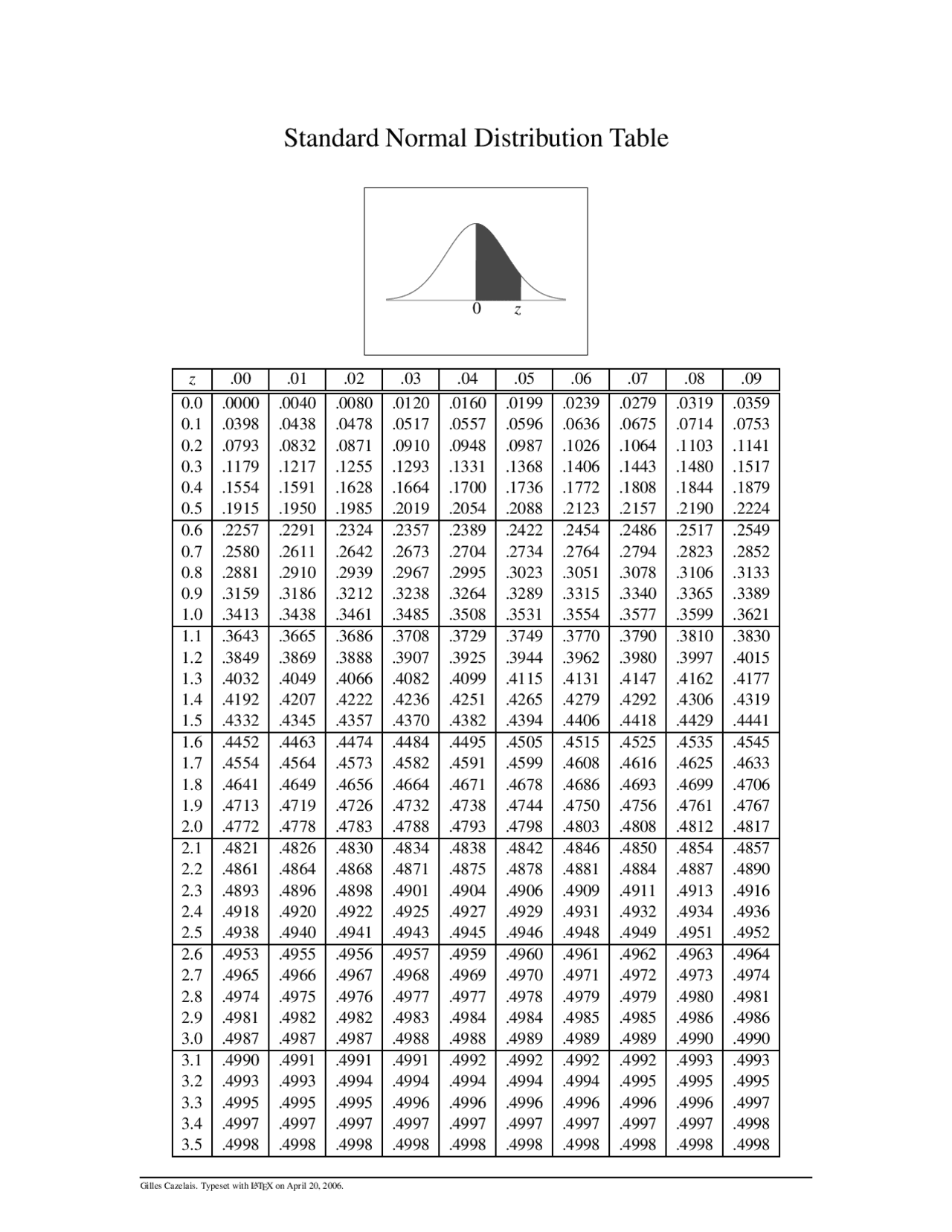
Construction and Interpretation of the Z-Desk (PDF):
The Z-table, typically obtainable in PDF format for simple entry and printing, sometimes presents cumulative possibilities. This implies it gives the likelihood {that a} randomly chosen worth from the usual regular distribution shall be lower than or equal to a given Z-score. The desk is often organized as follows:
- Rows: Symbolize those and tenths digits of the Z-score.
- Columns: Symbolize the hundredths digit of the Z-score.
- Desk Entries: Symbolize the cumulative likelihood (P(Z ≤ z)) akin to the Z-score shaped by the row and column values.
For instance, to search out the likelihood P(Z ≤ 1.96), you’ll:
- Find the row akin to 1.9.
- Find the column akin to 0.06.
- The intersection of this row and column gives you the cumulative likelihood. In most Z-tables, this worth shall be roughly 0.9750. This implies there is a 97.5% probability {that a} randomly chosen worth from the usual regular distribution shall be lower than or equal to 1.96.
Utilizing the Z-Desk for Completely different Chance Calculations:
The Z-table’s versatility extends past discovering easy cumulative possibilities. It may be used to calculate numerous different possibilities, together with:
-
Chance of Z being higher than a given worth: P(Z > z) = 1 – P(Z ≤ z). For instance, P(Z > 1.96) = 1 – 0.9750 = 0.0250.
-
Chance of Z being between two values: P(z1 ≤ Z ≤ z2) = P(Z ≤ z2) – P(Z ≤ z1). For instance, to search out P(-1 ≤ Z ≤ 1), you’ll subtract P(Z ≤ -1) from P(Z ≤ 1).
-
Discovering Z-scores akin to particular percentiles: If you’ll want to discover the Z-score that corresponds to, say, the ninetieth percentile, you’ll search for the closest likelihood worth to 0.90 within the desk after which establish the corresponding Z-score.
-
Purposes in Speculation Testing: The Z-table is essential in speculation testing involving the usual regular distribution. It is used to find out important Z-values for significance testing and calculating p-values.
-
Confidence Intervals: When developing confidence intervals for inhabitants means, the Z-table is employed to find out the suitable Z-score based mostly on the specified confidence degree.
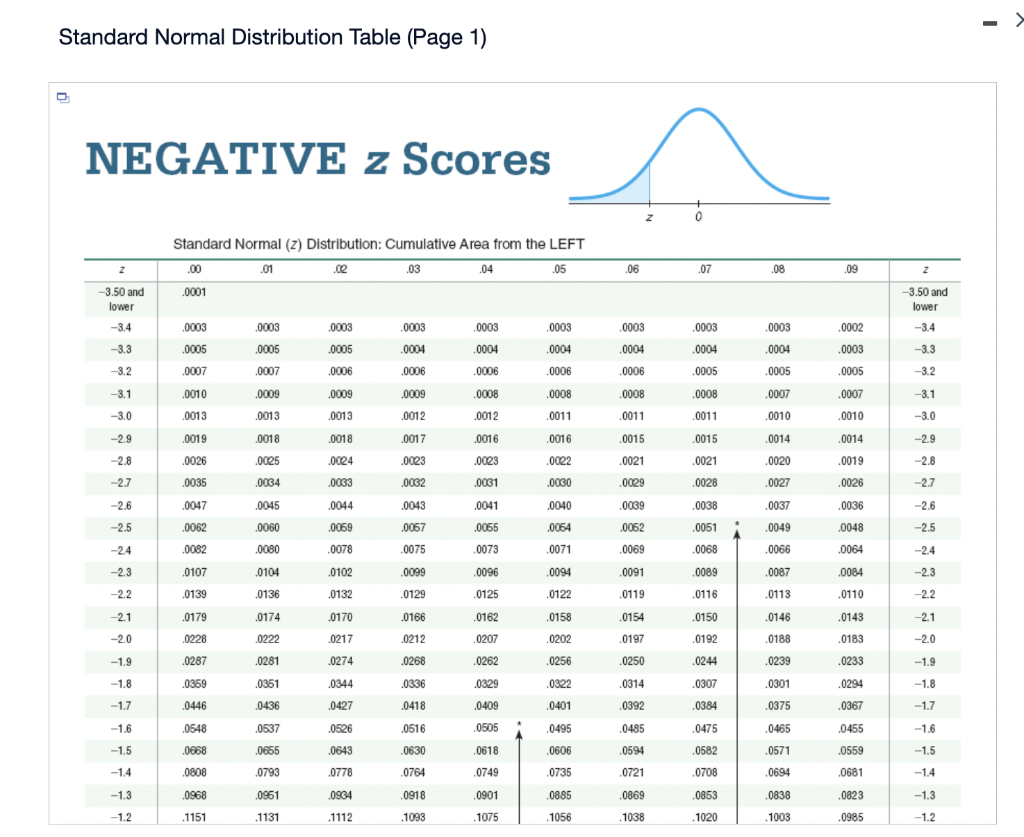
Coping with Unfavorable Z-scores:
The Z-table typically solely gives possibilities for constructive Z-scores. Nonetheless, the usual regular distribution is symmetric across the imply (0). Due to this fact, the likelihood of a Z-score being lower than a destructive worth is the same as the likelihood of a Z-score being higher than the constructive equal. For instance:
P(Z ≤ -1.96) = P(Z ≥ 1.96) = 1 – P(Z ≤ 1.96) = 1 – 0.9750 = 0.0250
Variations and On-line Z-Desk Calculators:
Whereas the usual Z-table format is broadly used, slight variations would possibly exist relying on the supply. Some tables would possibly current possibilities for the best tail (P(Z ≥ z)) as an alternative of the left tail (P(Z ≤ z)). All the time fastidiously verify the desk’s legend to know its particular presentation.
To keep away from guide lookup and potential errors, a number of on-line Z-table calculators can be found. These calculators let you enter a Z-score and immediately obtain the corresponding cumulative likelihood, saving time and enhancing accuracy.
Limitations and Issues:
Whereas the Z-table is a strong instrument, it is important to recollect its limitations:
-
Assumption of Normality: The Z-table is barely relevant when the info is generally distributed or roughly usually distributed (for bigger pattern sizes, the Central Restrict Theorem may also help justify this approximation). For non-normal information, different statistical strategies are obligatory.
-
Inhabitants Parameters: The Z-table requires data of the inhabitants imply (μ) and normal deviation (σ). If these parameters are unknown, the t-distribution and t-table must be used as an alternative.
-
Accuracy: The Z-table gives possibilities to a sure degree of precision. For very exact calculations, extra refined statistical software program may be obligatory.
Conclusion:
The Z-table is a useful useful resource for anybody working with statistical evaluation involving usually distributed information. Understanding its construction, interpretation, and purposes is essential for precisely calculating possibilities, conducting speculation checks, and developing confidence intervals. Whereas on-line calculators present handy options, an intensive understanding of the Z-table and its underlying rules stays important for a deep grasp of statistical ideas and their sensible implications. Mastering the Z-table empowers you to confidently navigate a variety of statistical issues and draw significant conclusions from information. By combining the data of this highly effective instrument with a strong understanding of statistical rules, you’ll be able to unlock the potential of information evaluation and make knowledgeable selections based mostly on proof.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Decoding the Z-Desk: A Complete Information to the Normal Regular Distribution Chart. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!