The Bar Chart: A Basis Of Knowledge Visualization
The Bar Chart: A Basis of Knowledge Visualization
Associated Articles: The Bar Chart: A Basis of Knowledge Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to The Bar Chart: A Basis of Knowledge Visualization. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Bar Chart: A Basis of Knowledge Visualization
The bar chart, a seemingly easy but remarkably versatile device, stands as a cornerstone of information visualization. Its effectiveness lies in its capability to obviously and concisely talk the relative magnitudes of various classes or teams of information. From easy comparisons of gross sales figures to advanced analyses of demographic tendencies, the bar chart’s adaptability makes it a staple in numerous fields, together with enterprise, science, training, and journalism. This text will delve into the nuances of bar charts, exploring their differing types, purposes, greatest practices, and limitations.
Understanding the Fundamentals:
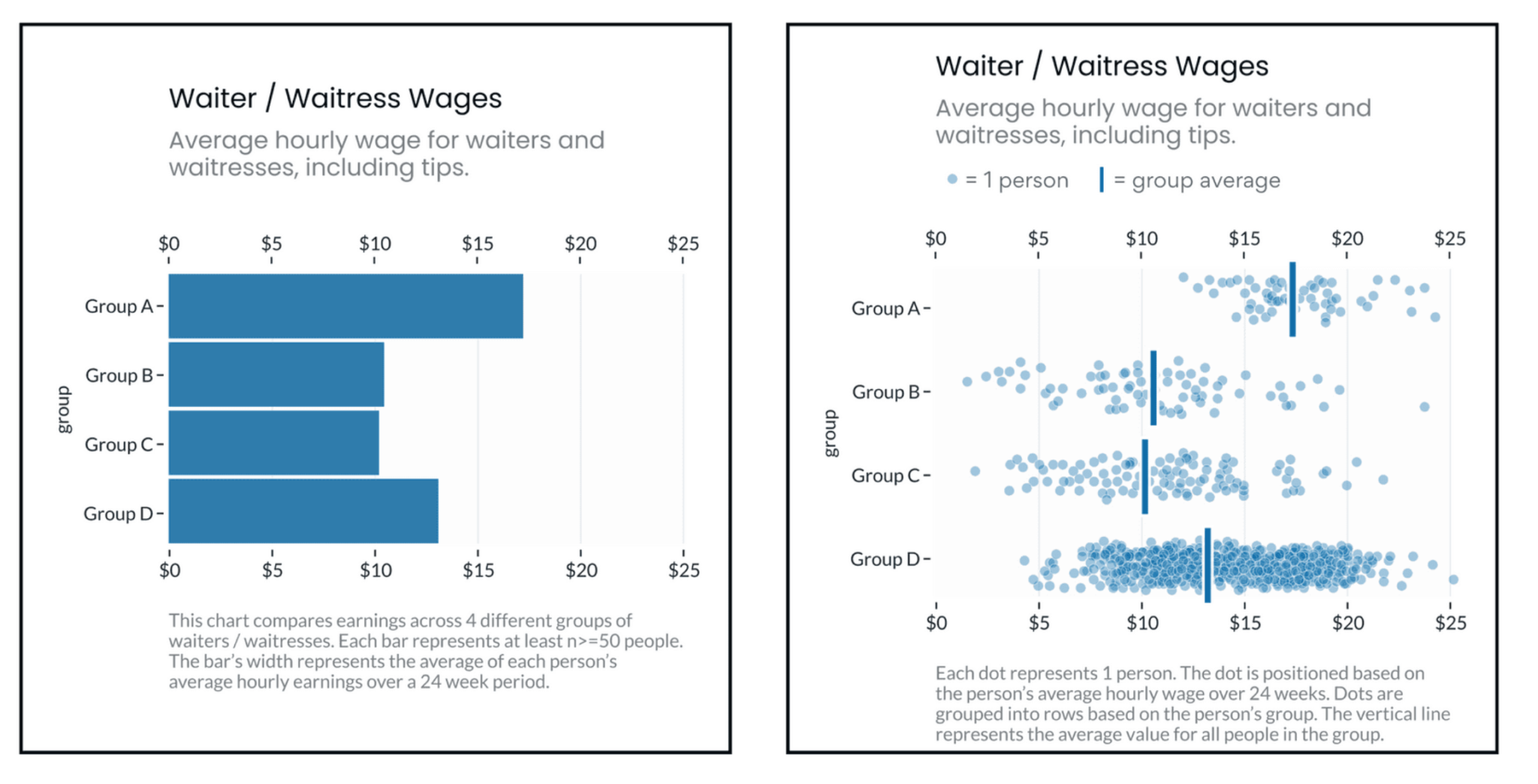
At its core, a bar chart makes use of rectangular bars of various lengths to symbolize the values of various classes. The size of every bar is instantly proportional to the worth it represents. The classes are sometimes displayed alongside the horizontal (x) axis, whereas the values are represented alongside the vertical (y) axis. This easy but efficient construction permits for fast and intuitive interpretation of information. For example, an extended bar instantly signifies a bigger worth in comparison with a shorter bar representing a smaller worth. This visible comparability eliminates the necessity for laborious numerical evaluation, making the knowledge readily accessible to a broad viewers.
Forms of Bar Charts:
Whereas the elemental precept stays constant, bar charts are available numerous varieties, every tailor-made to particular information illustration wants:
-
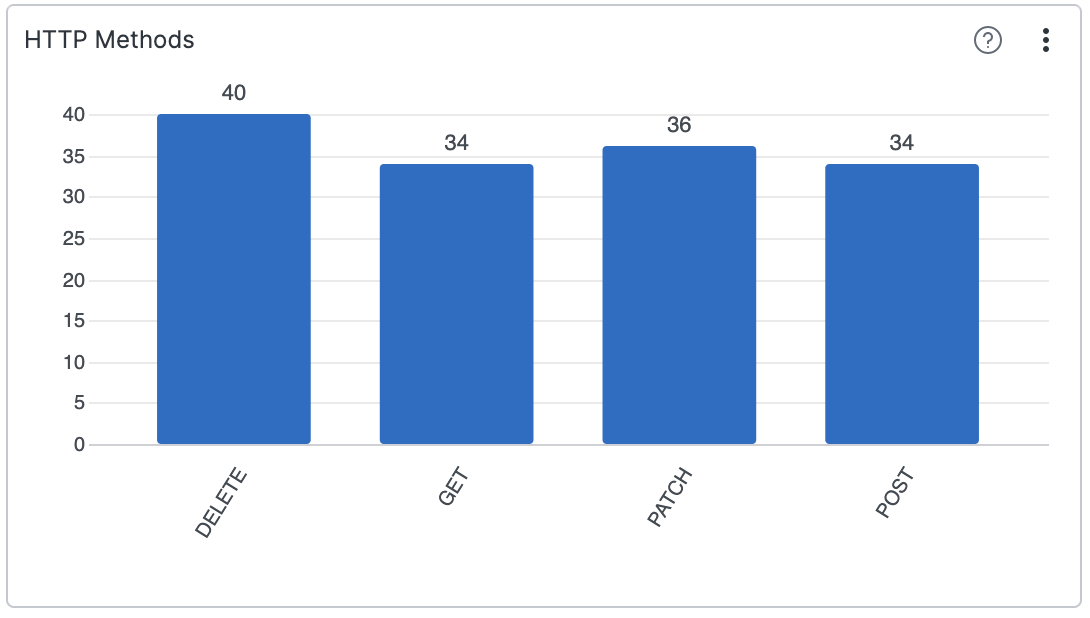
Vertical Bar Charts (Column Charts): That is the commonest sort, the place bars are oriented vertically. The classes are listed alongside the horizontal axis, and the values are represented by the peak of the bars. This orientation is usually most popular when coping with a lot of classes, because it permits for higher readability and avoids overlapping labels.
-
Horizontal Bar Charts: In distinction, horizontal bar charts place the classes alongside the vertical axis and the values alongside the horizontal axis. The size of the bars represents the magnitude of the values. This orientation is commonly most popular when coping with lengthy class labels, because it prevents them from overlapping and improves readability. They’re additionally significantly helpful when evaluating a small variety of classes throughout a number of values.
-
Grouped Bar Charts: These charts enable for the comparability of a number of variables inside every class. For instance, you may group bars representing gross sales figures for various merchandise throughout a number of areas. This grouping helps in analyzing the interaction between completely different variables and figuring out tendencies inside particular classes. Clear labeling and a legend are essential for deciphering grouped bar charts successfully.
-
Stacked Bar Charts: Just like grouped bar charts, stacked bar charts symbolize a number of variables inside every class. Nonetheless, as an alternative of putting the bars side-by-side, the bars representing completely different variables are stacked on high of one another inside every class. This visualization highlights the composition of every class, exhibiting the contribution of every variable to the whole worth. Stacked bar charts are significantly helpful for exhibiting proportions or percentages inside every class.
-
100% Stacked Bar Charts: A selected sort of stacked bar chart the place the whole top of the stacked bars for every class is normalized to 100%. This emphasizes the relative proportions of every variable inside every class somewhat than their absolute values.
Functions of Bar Charts:
The flexibility of bar charts makes them relevant throughout a variety of fields and purposes:
-
Enterprise Analytics: Analyzing gross sales figures, market share, buyer demographics, and efficiency metrics.
-
Scientific Analysis: Evaluating experimental outcomes, visualizing information from surveys, and representing statistical distributions.
-
Social Sciences: Presenting demographic information, illustrating social tendencies, and evaluating survey responses.
-
Schooling: Demonstrating scholar efficiency, illustrating the distribution of grades, and evaluating check scores.
-
Journalism: Speaking statistical data clearly and concisely, visually representing advanced information for information stories.
-
Finance: Displaying inventory costs, evaluating funding returns, and illustrating monetary efficiency.
Greatest Practices for Creating Efficient Bar Charts:
Creating a transparent and informative bar chart requires cautious consideration of a number of design parts:
-
Clear and Concise Labels: Use clear and concise labels for each axes and the legend (if relevant). Keep away from jargon and make sure the labels are simply comprehensible.
-
Acceptable Scale: Select a scale that precisely displays the information with out distorting the visible illustration. Keep away from unnecessarily massive or small scales that may misrepresent the information.
-
Constant Bar Width: Preserve constant bar widths all through the chart to keep away from visible bias.
-
Acceptable Shade Palette: Use a shade palette that’s each aesthetically pleasing and functionally efficient. Think about using shade to spotlight key information factors or to distinguish between classes.
-
Minimalist Design: Keep away from cluttering the chart with pointless parts. Concentrate on presenting the information clearly and concisely.
-
Knowledge Supply and Context: At all times embrace a transparent indication of the information supply and related context to make sure transparency and correct interpretation.
-
Accessibility: Make sure the chart is accessible to customers with disabilities, utilizing acceptable shade distinction and different textual content descriptions.
Limitations of Bar Charts:
Regardless of their versatility, bar charts have limitations:
-
Restricted to Categorical Knowledge: Bar charts are greatest suited to representing categorical information. They’re much less efficient for representing steady information, the place line charts or scatter plots could be extra acceptable.
-
Issue with Giant Datasets: Whereas grouped and stacked bar charts can deal with a number of variables, they will develop into cluttered and tough to interpret when coping with a really massive variety of classes or variables.
-
Potential for Misinterpretation: Incorrect scaling or deceptive labels can result in misinterpretations of the information. Cautious consideration to design particulars is essential to keep away from this.
-
No Indication of Correlation: Bar charts don’t inherently present correlations between completely different classes or variables. Different chart varieties, similar to scatter plots, are extra appropriate for visualizing correlations.
Conclusion:
The bar chart, regardless of its obvious simplicity, is a strong device for information visualization. Its capability to obviously talk the relative magnitudes of various classes makes it a worthwhile asset in numerous fields. By understanding the several types of bar charts, following greatest practices in design, and acknowledging their limitations, one can successfully leverage this versatile device to create compelling and informative visualizations that successfully talk information insights. The important thing to success lies in selecting the suitable sort of bar chart, fastidiously designing the visible parts, and presenting the knowledge in a transparent, concise, and accessible method. By doing so, bar charts can function a strong means of reworking uncooked information into actionable information.

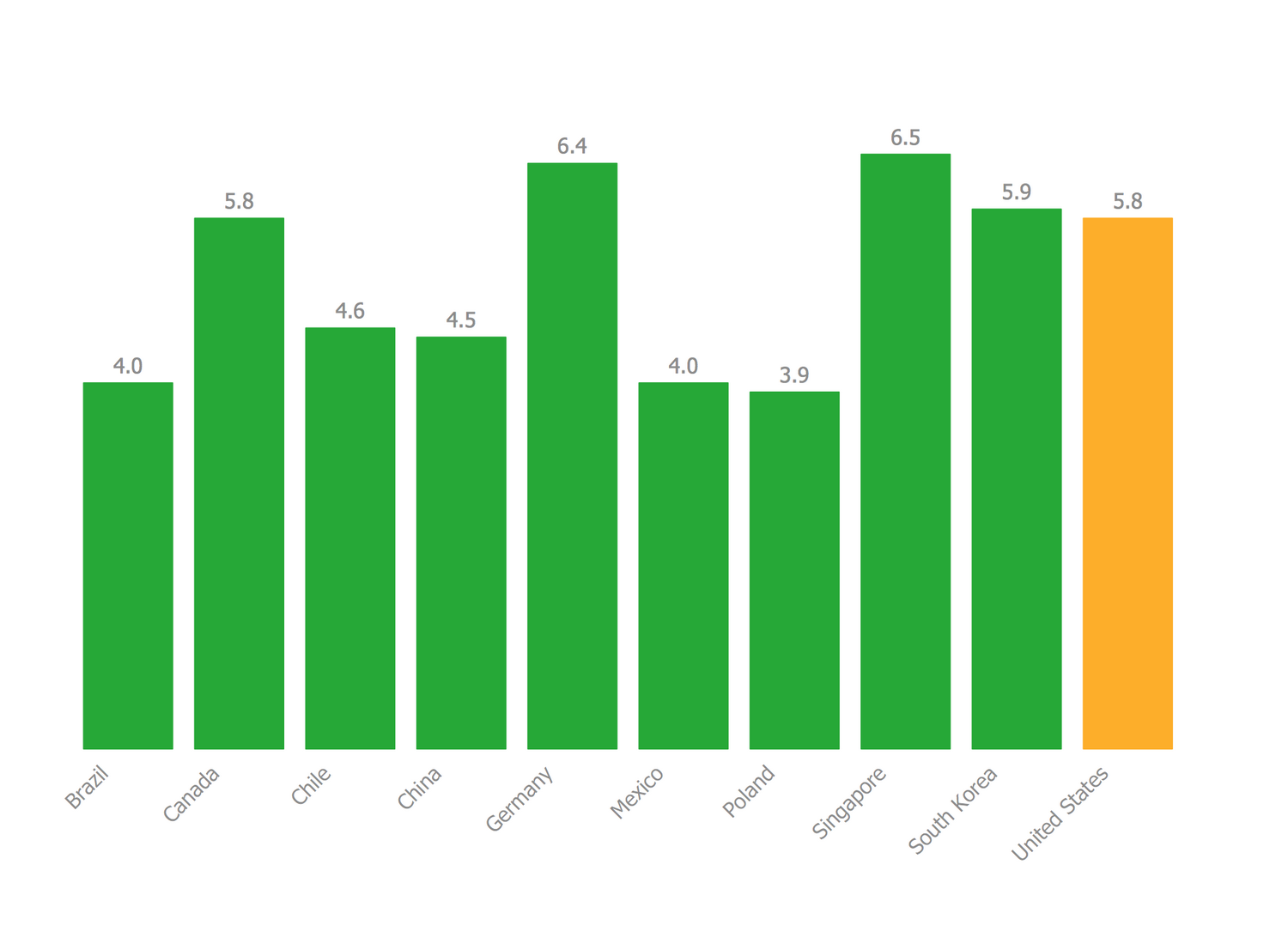
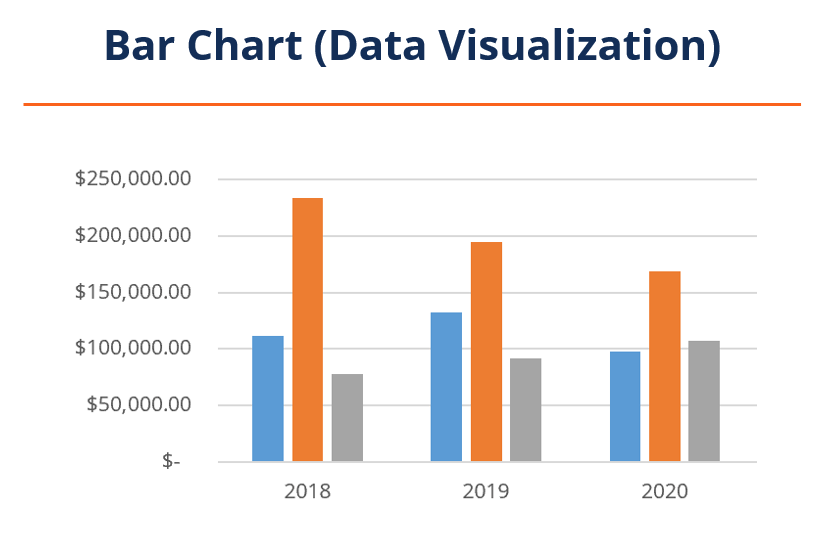
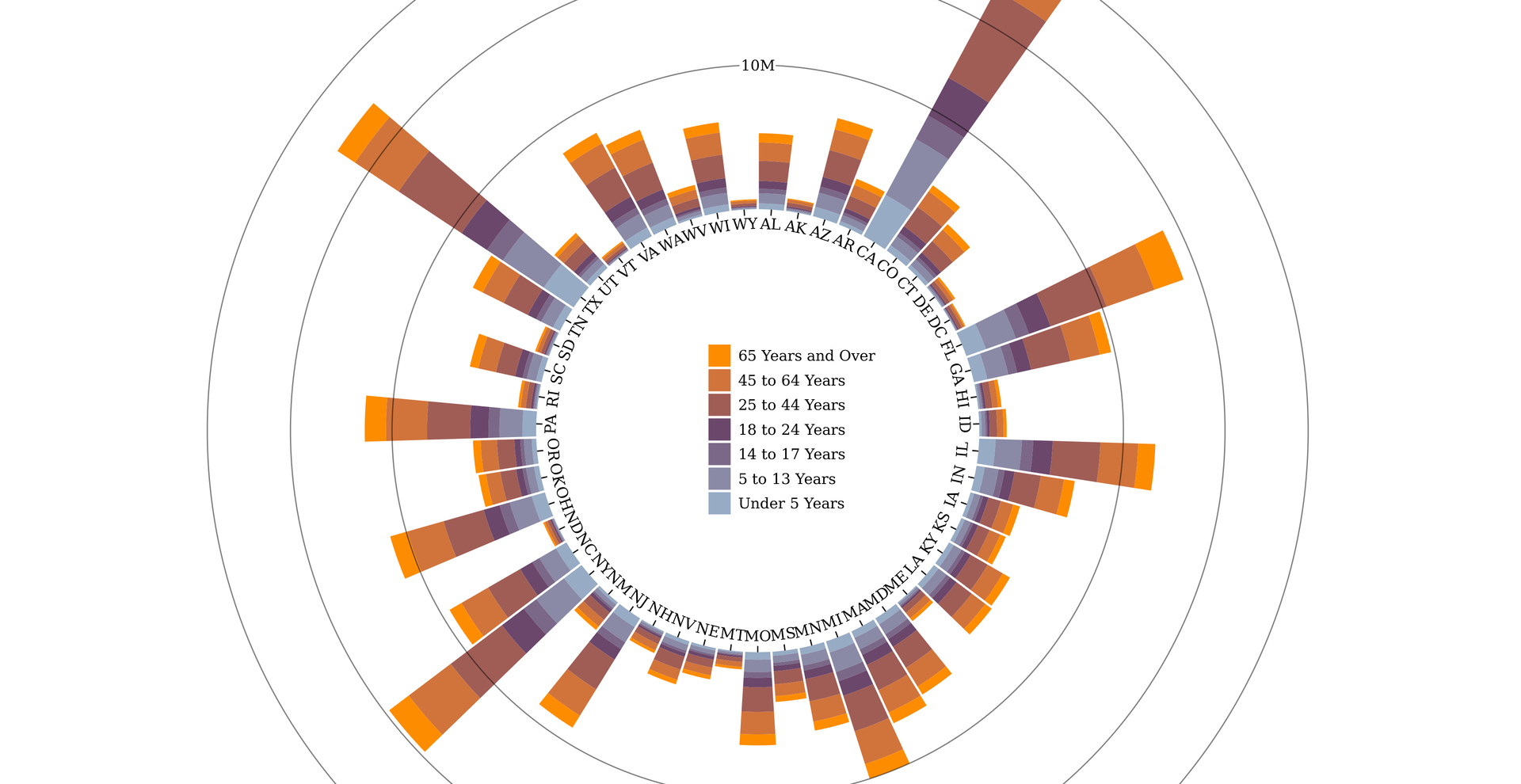
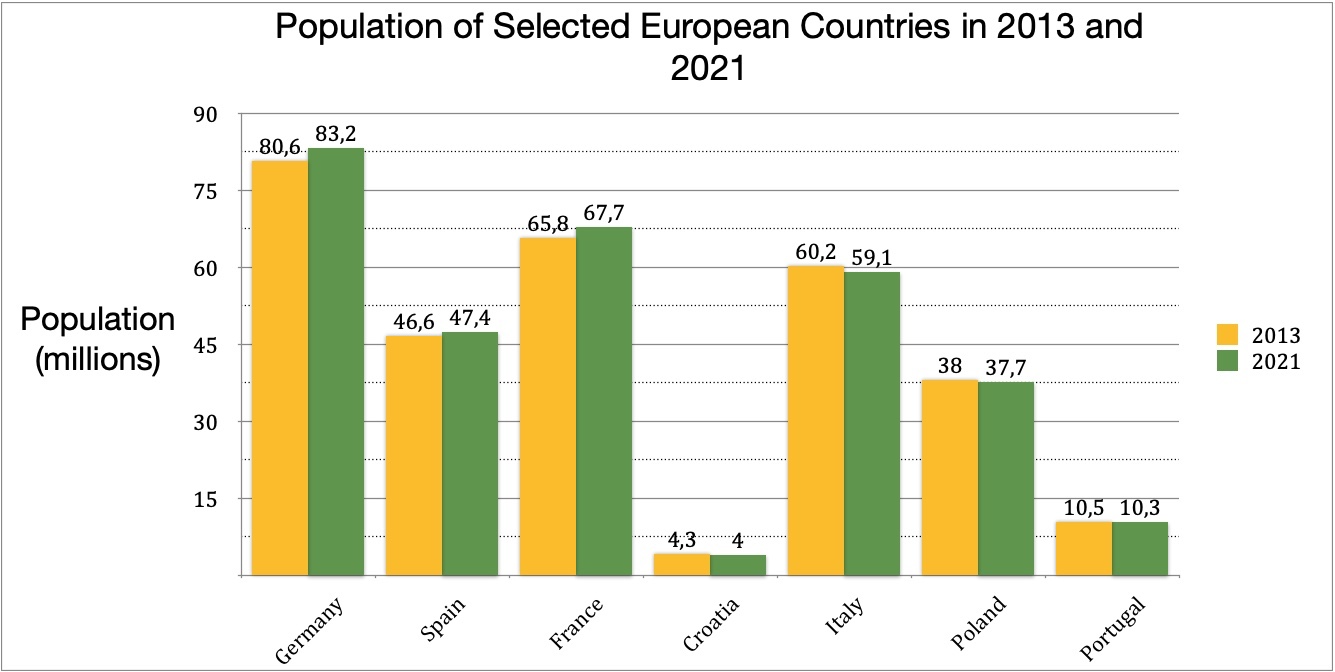

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into The Bar Chart: A Basis of Knowledge Visualization. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!
